config 配置文件加载
简介
同志们,这章我们来看一哈: Laravel 中 config 的加载原理。
上一章说过,Laravel 启动引导,无非就是循环实例化$bootstrappers 数组中的类,并调用类的 bootstrap 方法。
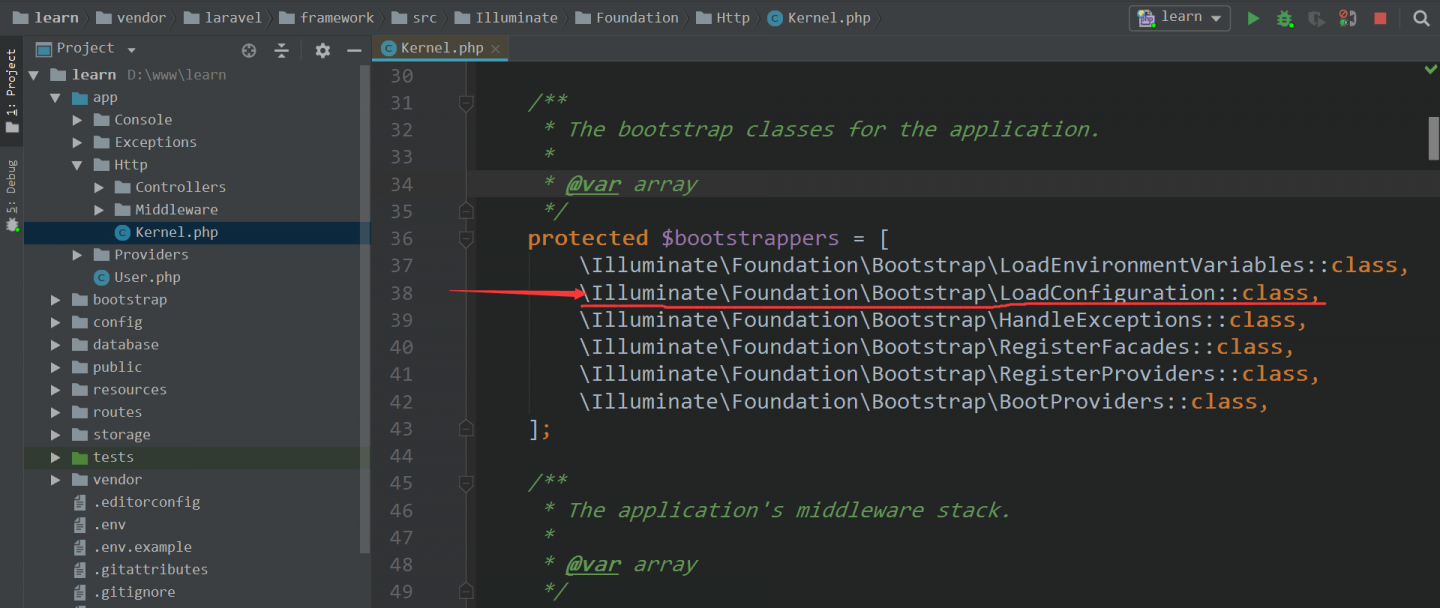
如图,这一章介绍划红线的 bootstrap 方法。
正文
先把 bootstrap 方法贴出来,我们一起来看看它长什么样
public function bootstrap(Application $app)
{
$items = [];
if (file_exists($cached = $app->getCachedConfigPath())) {
$items = require $cached;
$loadedFromCache = true;
}
$app->instance('config', $config = new Repository($items));
if (! isset($loadedFromCache)) {
$this->loadConfigurationFiles($app, $config);
}
$app->detectEnvironment(function () use ($config) {
return $config->get('app.env', 'production');
});
date_default_timezone_set($config->get('app.timezone', 'UTC'));
mb_internal_encoding('UTF-8');
}
- 第一个
$items = [];,初始化一个空数组,太简单了。。。有点侮辱智商。。。 - 第二个
if (file_exists($cached = $app->getCachedConfigPath())) {
$items = require $cached;
$loadedFromCache = true;
}
有木有缓存文件呀,有的话,包含执行,将返回的数组赋值给 $items ,并将 $loadedFromCache 赋值为 true。注:$app->getCachedConfigPath() 返回的缓存文件路径为 bootstrap/cache/config.php。
- 第三个
$app->instance('config', $config = new Repository($items));
这个就是 Laravel 实现配置管理的核心了。将所有加载好的配置内容赋值给容器的 instances 属性,用的时候取就行了。先撇一眼加载完的图,过过 "眼瘾"。。。
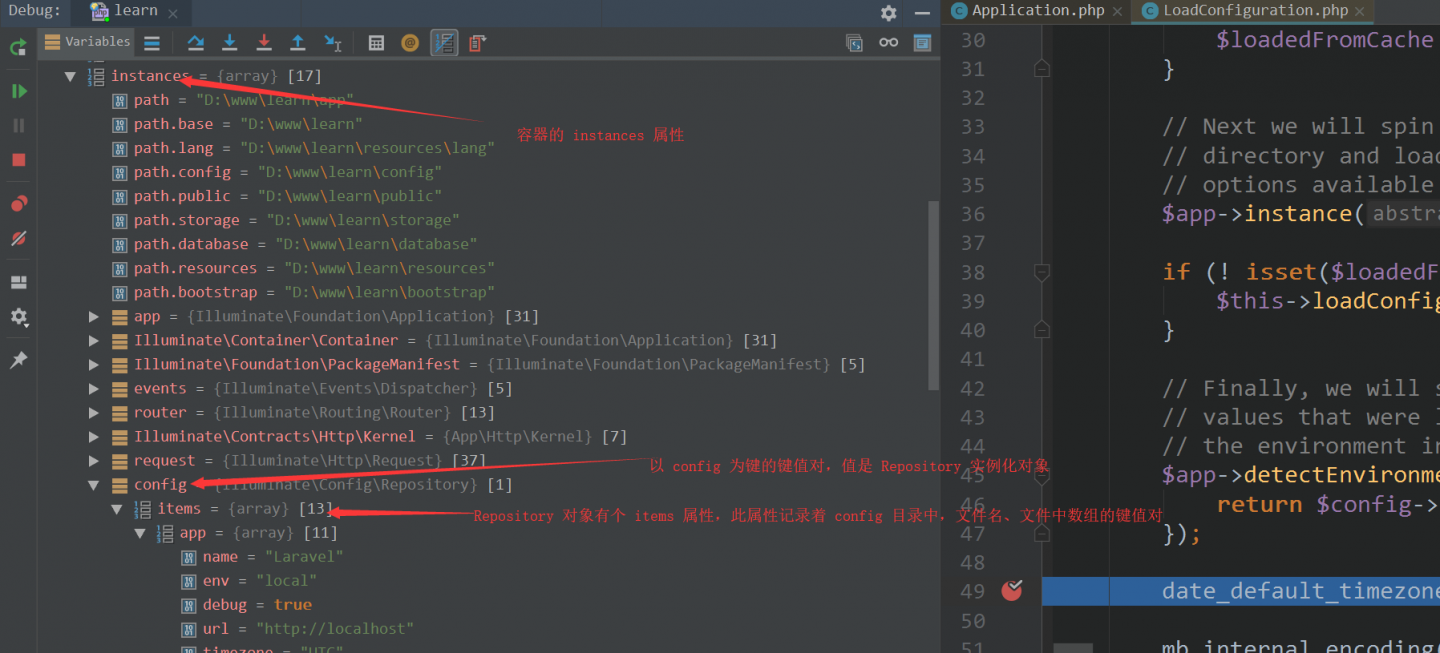
这时候你肯定要问了,加载时,没有缓存文件 $items 不就是空数组啦吗?别急,接下来就是没缓存文件的处理程序
- 第四个
if (! isset($loadedFromCache)) {
$this->loadConfigurationFiles($app, $config);
}
这句就是没设置 $loadedFromCache 变量,就执行当前对象的 loadConfigurationFiles 方法。我的没缓存,所以就没设置 $loadedFromCache 变量,因此会执行 loadConfigurationFiles
loadConfigurationFiles 方法的具体作用,下面说。现在简单说一下它的功能:自动解析 config/ 目录下的 .php 文件,支持多层目录哦,然后,将所找到的 .php 文件包含执行,取返回的数组(里面是每个 php 文件的配置内容)
- 第五个
$app->detectEnvironment(function () use ($config) {
return $config->get('app.env', 'production');
});
检测当前执行环境是本地环境,还是生产环境。并通过容器的 bind 方法赋值给容器的bindings 属性
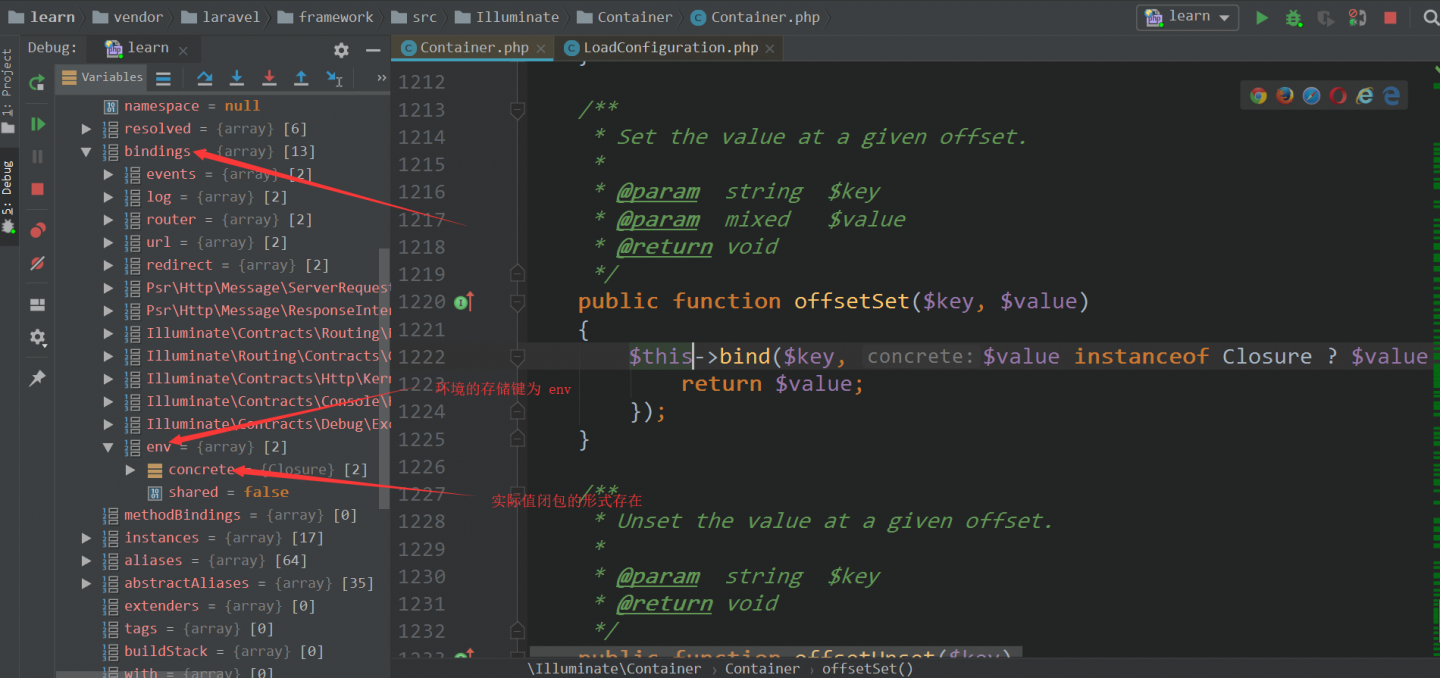
这个不是重点,大家了解一下就行了。
- 第六个
date_default_timezone_set($config->get('app.timezone', 'UTC'));
mb_internal_encoding('UTF-8');
根据 app.timezone 设置 Laravel 执行中的时区,并设置 Laravel 执行中的字符编码("UTF-8")
下面我们重点介绍一下 loadConfigurationFiles 方法
loadConfigurationFiles 方法
先贴出代码
protected function loadConfigurationFiles(Application $app, RepositoryContract $repository)
{
$files = $this->getConfigurationFiles($app);
if (! isset($files['app'])) {
throw new Exception('Unable to load the "app" configuration file.');
}
foreach ($files as $key => $path) {
$repository->set($key, require $path);
}
}
- 第一个
$files = $this->getConfigurationFiles($app);
这里面主要用到 了 PHP 的 SPL 基本扩展中的目录文件迭代器,循环过滤寻找需要的目录和 .php 文件,而调用这些迭代器的类是 Symfony 的 Finder 组件。
有兴趣的同学可以看这一下官网关于这个扩展的介绍 。。。点我进入
关于这个方法下面我会进入细讲
- 第二个
if (! isset($files['app'])) {
throw new Exception('Unable to load the "app" configuration file.');
}
如果删除了 config/app.php 文件,就会报这个异常
- 第三个
foreach ($files as $key => $path) {
$repository->set($key, require $path);
}
哈哈,这个就是在获取完所有配置文件路径后,正式往容器存储配置了,我们看一下 $files 变量长啥样
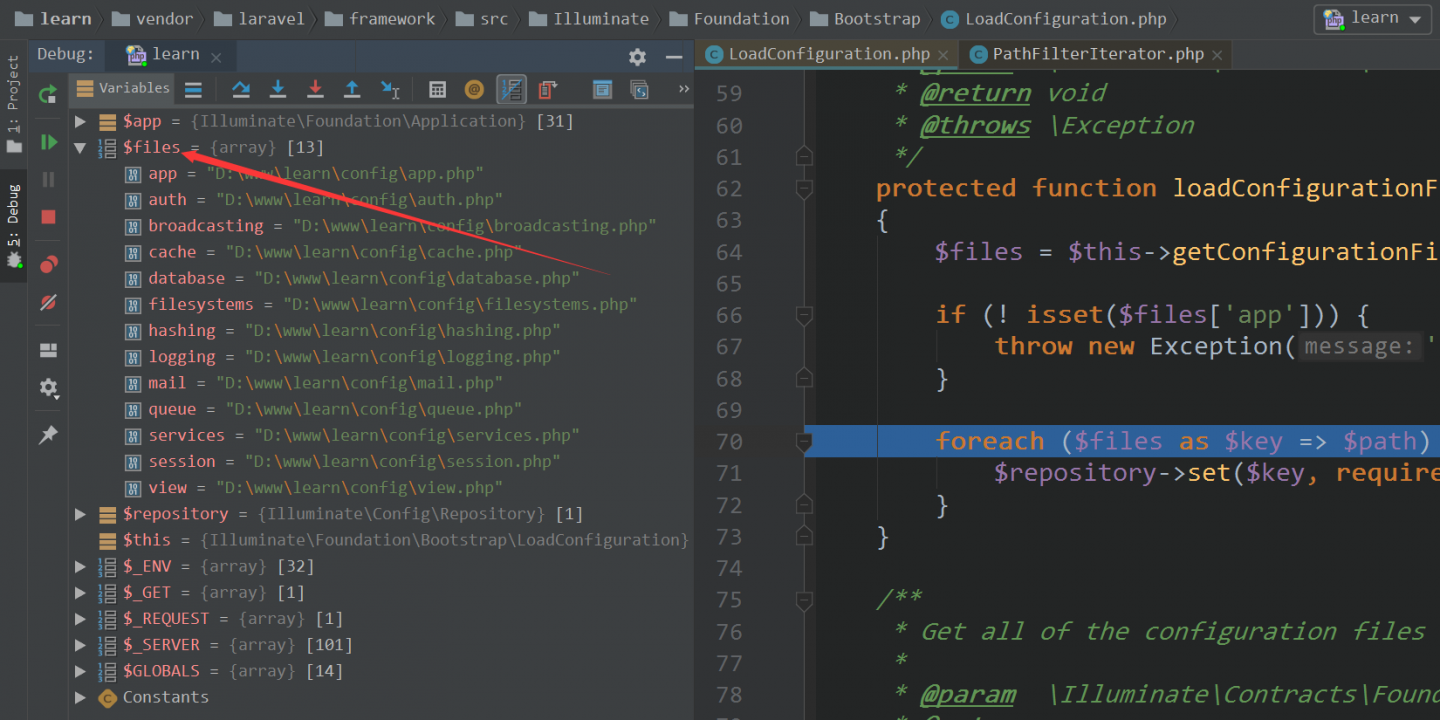
看到没,无非就是一个数组,数组的键是 .php 的文件的名字,值是 .php 文件的绝对路径;通过包含执行,取出返回的数组(这个数组,是每个 .php 文件的具体配置内容)。之后赋值给 Repository 类的 items 属性,这样容器 instances 属性中的 config 键指向的值就会是处理好的配置内容;
为什么会这样呢,instances 属性赋值是在之前的赋值的呀。这就是 引用数据 类型的特性了:引用类型实际存储的是数据的指针,多个变量名存储不同变量值,这个变量值实际是引用数据的指针,它们都指向同一个数据源(堆中的对象源数据);一变皆变,一动皆动。。。
下面我们看一下 getConfigurationFiles 方法
getConfigurationFiles 方法
老规矩,先贴代码
protected function getConfigurationFiles(Application $app)
{
$files = [];
$configPath = realpath($app->configPath());
foreach (Finder::create()->files()->name('*.php')->in($configPath) as $file) {
$directory = $this->getNestedDirectory($file, $configPath);
$files[$directory.basename($file->getRealPath(), '.php')] = $file->getRealPath();
}
ksort($files, SORT_NATURAL);
return $files;
}
- 第一个,
$files = [];,额。。。有点侮辱智商 - 第二个
$configPath = realpath($app->configPath());
将 config/ 的标准(没有 ../)绝对路径赋值给 $configPath
- 第三个
foreach (Finder::create()->files()->name('*.php')->in($configPath) as $file) {
$directory = $this->getNestedDirectory($file, $configPath);
$files[$directory.basename($file->getRealPath(), '.php')] = $file->getRealPath();
}
这个地方就是调用了 Symfony 的 Finder 组件进行 .php 文件寻找了。
大家看这个
Finder::create()->files()->name('*.php')->in($configPath)
这个这一串,返回的是 Finder 类对象本身,但是。。。这个 Finder 类对象是一个迭代器,所以能够进行 foreach 循环,我们看一下最后这个 in 方法
public function in($dirs)
{ // $dirs: "D:\www\learn\config"
$resolvedDirs = array();
foreach ((array) $dirs as $dir) {
if (is_dir($dir)) {
$resolvedDirs[] = $this->normalizeDir($dir);
} elseif ($glob = glob($dir, (\defined('GLOB_BRACE') ? GLOB_BRACE : 0) | GLOB_ONLYDIR)) {
$resolvedDirs = array_merge($resolvedDirs, array_map(array($this, 'normalizeDir'), $glob));
} else {
throw new \InvalidArgumentException(sprintf('The "%s" directory does not exist.', $dir));
}
}
$this->dirs = array_merge($this->dirs, $resolvedDirs);
return $this;
}
乱七八糟的一堆,看的我头疼。。。其实那么多,在这里就实现一个功能:给当前对象的属性 dirs 赋值,看一图就知道了
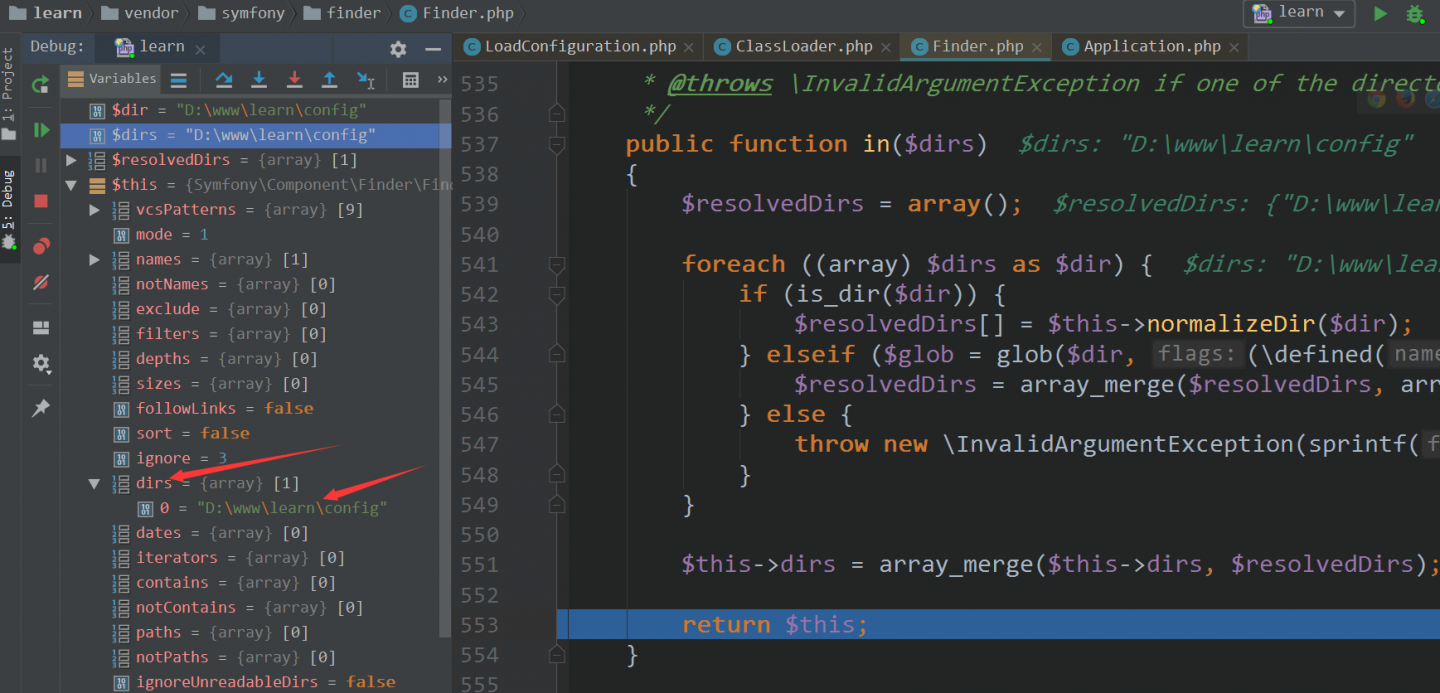
然后呢。。。返回了 $this ,上面说过的,当前对象是一个目录文件迭代器对象,能进行 foreach 循环,其元素就是对象中 current 方法的返回值。在运行这个目录文件迭代器时,加入了一堆过滤操作,如过滤掉 ./ 和 ../ 这样的目录,还过滤掉了 .git、.svn、.hg、_svn 这样的目录。
因为 PHP 内置的这个 SPL 迭代器基本扩展,功能很强劲,文档模模糊糊,大体知道支持目录层次循环,看 current 方法法的内容,也知道支持多层目录配置
- 第四个
ksort($files, SORT_NATURAL);
对 $files 数组进行自然序排序
- 第五个,返回
到这里 $files 算是拿到了,呼,这么长,就为了兼容各种情况,写了这么长,看的我一个头两个大。。。
写在最后
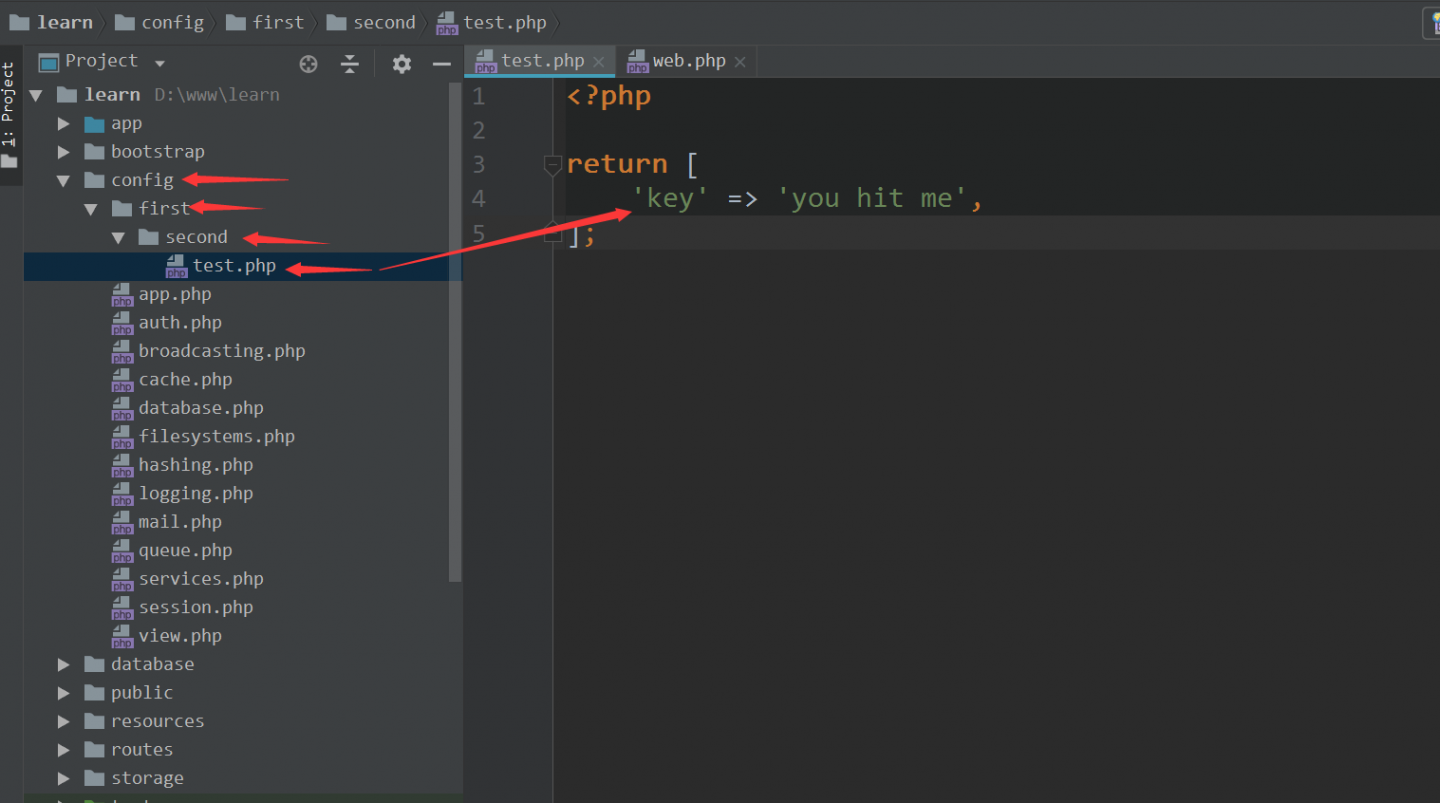
通过上面的学习我们知道了,配置文件支持多层目录,如下图,是一个多层目录配置的测试
- 定义深层目录的配置文件
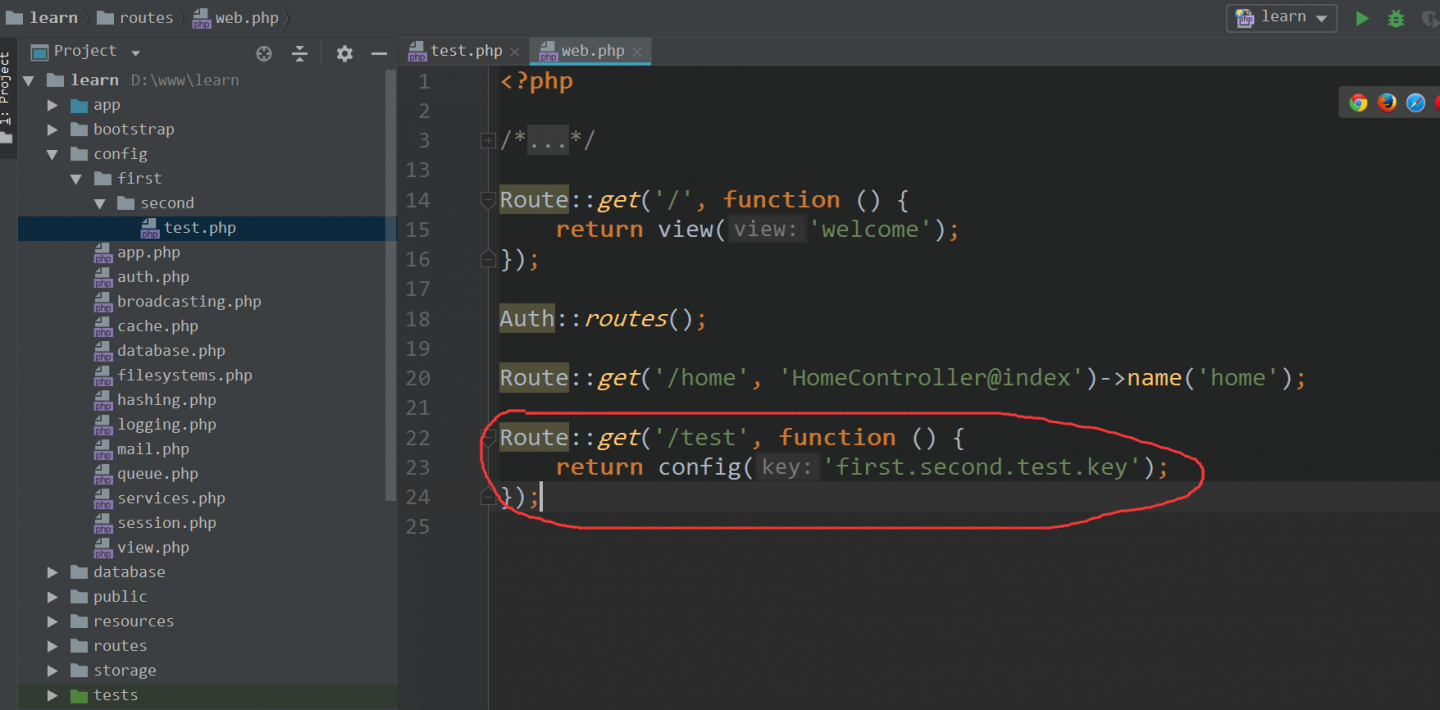
- 书写路由
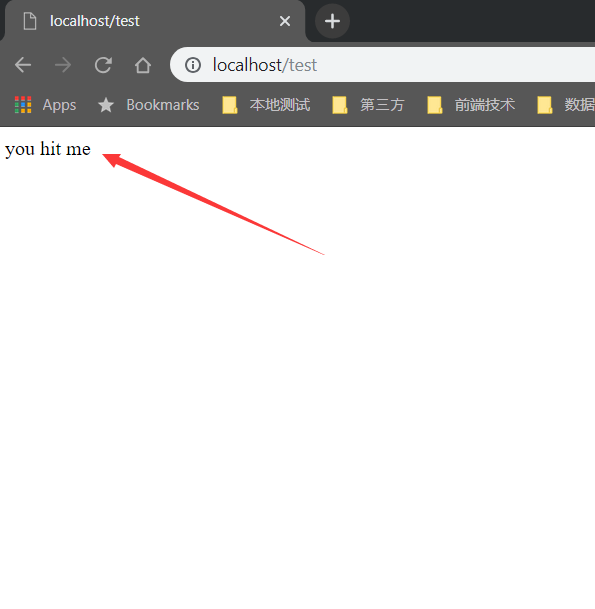
- 看浏览器返回
好了,今天的章节到这了,下一章,我们继续我们的 $bootstrappers 数组。。。